In discussions spanning numerous years, the concept of smart factories and Industry 4.0 has been a subject of interest, yet the tangible realization of their benefits can be achieved today through the utilization of industrial connectivity.
Industrial connectivity within manufacturing facilitates a diverse range of applications aimed at enhancing efficiency, elevating production quality, enabling real-time monitoring and control, and facilitating informed decision-making processes.
In reality, the attainment of several significant advantages associated with these ambitious visions and strategies is feasible by employing industrial connectivity to dismantle the conventional barriers prevalent in manufacturing.
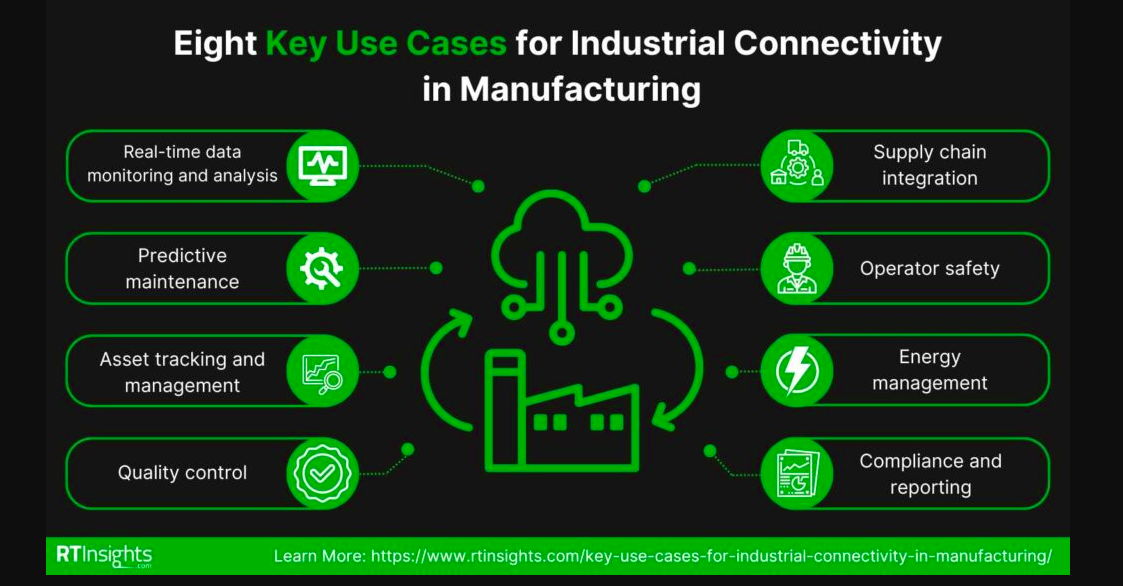
Indeed, numerous widely employed applications made possible by providing standardized access to data via industrial connectivity have yielded substantial impacts across manufacturing operations worldwide. Some of these pivotal applications include:
Real-time Data Monitoring and Analysis: Manufacturers routinely employ industrial connectivity to monitor equipment and production processes in real-time, enabling prompt adjustments to enhance efficiency, reduce wastage, and prevent downtime.
Predictive Maintenance: By scrutinizing data from sensors and machines obtained via connectivity solutions across a facility, predictive maintenance systems can anticipate potential equipment failures or maintenance requirements, averting unexpected breakdowns and prolonging machinery lifespan.
Asset Tracking and Management: Industrial connectivity facilitates the tracking of physical assets throughout the manufacturing process, thereby improving inventory management, minimizing losses, and optimizing the supply chain.
Quality Control: Automated systems and sensors can continuously monitor product quality, identifying defects or deviations from standards in real-time, ensuring the production of high-quality outputs.
Energy Management: Connectivity enables the monitoring and management of energy consumption across manufacturing operations, aiding in the identification of inefficiencies and opportunities for energy conservation.
Supply Chain Integration: Seamless data exchange among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors enhances supply chain visibility, enables just-in-time inventory practices, and reduces lead times.
Operator Safety: Wearable sensors and safety monitoring systems contribute to ensuring worker safety by detecting hazardous conditions, monitoring health indicators, and enforcing compliance with safety protocols.
Customization and Flexibility: Advanced connectivity and data analytics empower manufacturers to adapt more readily to changes in consumer demand, enabling greater flexibility in production lines and customization options.
Compliance and Reporting: Automated data collection via industrial connectivity and subsequent analysis facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and enable more accurate and timely reporting.
Advancing Operations to New Heights
These applications represent the readily achievable benefits of widespread industrial connectivity. Moreover, the technology paves the way for more advanced, forward-thinking applications geared towards strategic rather than operational objectives.
For instance, industrial connectivity serves as the foundation for smart factories and Industry 4.0, leveraging connectivity, big data, AI, and automation to establish highly efficient, self-optimizing production environments.
Another emerging area of interest is collaborative robotics environments, where robots connected to the manufacturing network operate alongside humans, learning and adapting to new tasks to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Furthermore, in light of lessons learned during the pandemic, many organizations have discovered that certain aspects of their operations can be conducted remotely. Industrial connectivity facilitates the remote monitoring and control of production processes by managers and technicians from distant locations, offering flexibility and rapid issue resolution capabilities.
Critical Technologies for Enabling These Applications
The implementation of industrial connectivity in manufacturing necessitates the integration of a diverse array of technologies working in synergy to collect, transmit, analyze, and act upon data throughout the manufacturing process.
Key technologies essential for manufacturers to effectively leverage industrial connectivity include:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices and sensors
- Edge computing
- Cloud computing
- Analytics and AI
- Cybersecurity solutions
- Wireless communication networks
- Digital twins
- SCADA and MES systems
Deploying these technologies mandates meticulous planning, investment, and a strategic approach to digital transformation. It entails not only technological upgrades but also cultural shifts, process optimizations, and workforce skills development initiatives.
This article was originally published on rtinsights. Read the orignal article.
FAQs
- What is industrial connectivity, and why is it important in manufacturing?Industrial connectivity refers to the integration of digital technologies and communication networks within manufacturing environments. It is important for driving efficiency, enhancing productivity, and fostering innovation in modern manufacturing.
- How does industrial connectivity enable real-time data monitoring and analysis?Industrial connectivity enables the seamless exchange of data between machines, equipment, and systems, allowing manufacturers to monitor equipment and production processes in real time and make informed decisions to optimize efficiency and minimize downtime.
- What are some examples of predictive maintenance enabled by industrial connectivity?Predictive maintenance systems analyze data from sensors and machines to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance interventions and preventing costly unplanned downtime.
- How does industrial connectivity contribute to supply chain integration?Industrial connectivity facilitates real-time data exchange across the supply chain, enabling just-in-time inventory practices, reducing lead times, and improving supply chain visibility and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- What technologies are essential for implementing industrial connectivity in manufacturing?Key technologies include Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices and sensors, edge computing, cloud computing, analytics and AI, cybersecurity solutions, wireless communication networks, digital twins, and SCADA and MES systems.